Rate and Review render farm RANCH Computing
RANCH Computing is a high-performance rendering service for CPU and GPU projects and also a provider of hardware solutions dedicated to 3D rendering. RANCH Computing began its activity in March 2007 and is based in Paris, France Since then, Ranch Computing’s aim is to allow any graphic designers, whatever line of business they are in (animation, VFX, architecture, design, video games…), to tackle the rendering process serenely in order to meet their deadlines and their budgets. The business model that RANCH Computing is following is based on SaaS (Software-as-a-Service). This allows customers to have easy access to the RANCH Computing farm and utilize the power of render nodes to speed up the rendering process.

|
Company Name |
RANCH Computing |
|
Website |
|
|
Country |
France |
|
Type of render farm |
CPU and GPU |
|
Free Trial |
30 € free trial for new users |
Interface
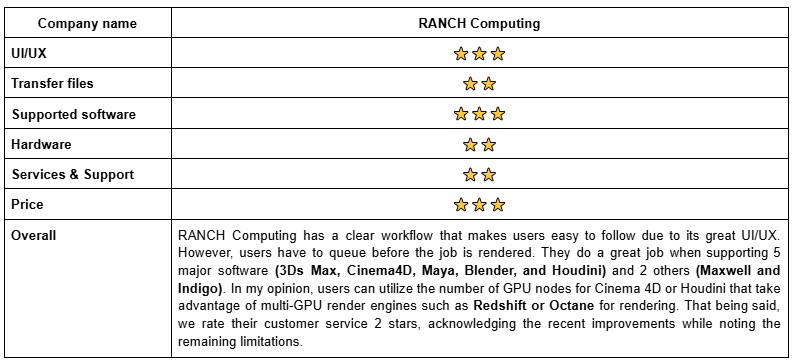
Firstly, we take a look at the RANCH Computing website and dashboard that they offer their customers. It is evident that their UI/UX is quite clear and friendly for users to start using RANCH Computing services. They make clear each category in the dashboard for each step. To illustrate, in the queue part, users will know how many jobs are being queued, or how many jobs are currently being rendered at a specific percentage of the rendering process. Besides, users also know these jobs are being rendered on CPU farm or GPU farm, as well as the type of software used. The serious drawback in RANCH Computing is that users have to queue before being served on the RANCH farm, you may be vague when waiting for your turn and do not know how long it will take. Regarding your job, to ensure that your project will be rendered as you expect on the RANCH, it needs to be well prepared on your computer. This is the goal of the RANCHecker, a free and simple tool. This plugin will gather all assets used by your scene, verify the rendering parameters, change file paths if necessary, and warns you in case of possible issues (incompatible plugin for instance). Now RANCHecker is currently available for the following software: 3Ds Max, Cinema4D, Maya, and Blender. The rest of the workflow on RANCH Computing is Uploading your files, Waiting for the queue list, Rendering and Downloading your results.
However, you are currently able to send a job with under 50GB of data. Rendering very heavy projects put a lot of strain on the RANCH systems, it is therefore mandatory to contact RANCH before submitting any project bigger than 50 GB (uncompressed size of archive generated by the RANCHecker) to check whether RANCH is possible to render your project or not. In addition to the limited storage, The Ranch does currently not support frame numbers greater than 9999.
Support software
In terms of supported software, RANCH Computing gives the list of major software namely 3Ds Max, Cinema4D, Maya, Blender, and Houdini. Moreover, RANCH is highly recommended for Maxwell and Indigo software which is randomly offered by well-known render farms. One of the greatest advantages of RANCH is they support a wide range of software versions, renderers, and plugins for users that allow them to have many options to select.
Both CPU vs GPU rendering, RANCH gives us to select the latest versions of render engines for the aforementioned software. When it comes to 3Ds Max renderers, there are Arnold, ART, Corona, Vray, Scanline for CPU-based rendering while Arnold GPU, Vray GPU, Redshift, and FStorm for GPU-based rendering. With Cinema4D, you can use Vray, Corona, Arnold for CPU jobs, and Redshift, Octane, Arnold for GPU jobs. Maya is supported with fewer options when Vray, Arnold, and Maxwell are used for CPU-based rendering, while the only Redshift, Vray is used for that of GPU. For Blender, aside from the built-in renderers such as Cycles and Eevee, RANCH also supports Redshift, which is not commonly available across many render farms. For Houdini, in addition to the native renderers integrated in the software, RANCH extends support to Redshift and Arnold, giving users more flexibility for production-level rendering.
Hardware
Hardware is the decisive factor for each render farm to speed up the rendering process. Regarding RANCH Computing, they provide both CPU and GPU-based rendering.
First, we would like to mention the type of CPU on the RANCH Computing farm. Ranch Computing offers powerful AMD CPUs (Turin, Bergamo, Milan) on virtual machines. Their configurations include 42 vCPU with 160 GB RAM, 84 vCPU with 240 GB RAM, and 168 vCPU with 480 GB RAM, all supporting up to 512 threads and 1.5 TB RAM, NVMe storage from 250 GB to 1.5 TB, and 25 Gbps network connectivity. You can select the priority level, including CPU-Low, CPU-Medium, and CPU-High, for which the number of render nodes ranges from 24 to 64
Next, Ranch Computing now offers the latest RTX 3090, RTX 4090, and the powerful RTX 5090 GPUs. The RTX 5090 is currently the most powerful GPU on the market, delivering exceptional rendering speed and stability for demanding 3D, VFX, and animation projects. Moreover, you can leverage the number of render nodes that RANCH offers you to speed up your render time. It is because you are likely to select a maximum of 10 nodes for GPU-Low, 20 nodes for GPU-Medium, and 30 nodes for GPU-High.
Pricing
There is no doubt that pricing has an important impact on the ranking render farm list. With RANCH Computing, they offer us a wide variety of price plans depending on the priority level we choose. To commence, the CPU prices are based on the commonly accepted ‘Gigahertz-Hour’ (GHz.h) unit which means the cost of a project is based on how many GHz.h are used to render it. For instance,
- An AMD 42-Core Server has 42 cores and a clock frequency of 2.45 GHz.
- If such a server renders for 2 hours, the number of GHz.h charged will be 42 cores x 2.45 GHz x 2 hours = 205.8 GHz.h.
- If you are using a server with the CPU-Low priority (0.011 RC/GHz.h) for 2 hours, the cost will be 205.8 GHz.h × 0.011 RC/GHz.h = 2.26 RC.
- If 30 identical machines render simultaneously: 2.26 RC × 30 machines = 67.8 RC
Cost by Priority
| Priority | Price per GHz.h | Cost for 205.8 GHz.h |
| CPU-Low | 0.011 RC | 2.26 RC |
| CPU-Medium | 0.013 RC | 2.67 RC |
| CPU-High | 0.015 RC | 3.09 RC |
In contrast, the GPU prices are based on the commonly accepted “OctaneBench-hour” unit which means the cost of a project is based on how many OB.h are used to render it. For example,
- A GPU with 2 x RTX 3090 has an OctaneBench score of ~1300 points (based on OctaneBench 2020/2025).
- If such a server renders for a half-hour, the number of OB.h charged will be 1300 OB × 0.5 h = 650 OB.h.
- If you are using a server with the GPU-Low priority 0.005 RC/OB.h) for a half-hour, the cost will be 650 OB.h × 0.005 RC/OB.h = 3.25 RC.
- If 10 identical machines render simultaneously: 3.25 RC × 10 machines = 32.5 RC.
Cost by Priority
| Priority | Price per OB.h (in RC) | Cost for 650 OB.h |
| GPU Low | 0.005 RC | 3.25 RC |
| GPU Medium | 0.007 RC | 4.55 RC |
| GPU High | 0.010 RC | 6.5 RC |
General speaking, the price list that RANCH offers can be considered “reasonable” when compared to that of other render farms.
Support
Support is a crucial factor when evaluating any render farm. In the past, RANCH Computing was not highly appreciated in this area, but they have now improved by adding a direct live support channel on their website, making them more competitive with top render farms such as iRender, GarageFarm, Fox Renderfarm, and RebusFarm. However, their overall availability is still limited. RANCH provides support mainly during office hours – Monday to Friday, 9 a.m. to 7 p.m. (GMT+1, Paris) – and outside these hours, users can only reach them via email. While they sometimes respond within minutes, there are also cases where replies take much longer, and email remains their most reliable communication method.
Even with the new live support feature, RANCH’s response time is still slower compared to other leading render farms that offer real 24/7 instant support. For this reason, we rate their customer service 2 stars, acknowledging the recent improvements while noting the remaining limitations.
WE RANK

LATEST NEWS
The latest creative news





